See also: 体
| ||||||||
| ||||||||
Translingual
[edit]| Stroke order | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Han character
[edit]休 (Kangxi radical 9, 人+4, 6 strokes, cangjie input 人木 (OD), four-corner 24290, composition ⿰亻木)
Derived characters
[edit]- 𠁫, 咻, 𡜨, 恘, 𢫩, 㳜, 㹯, 𭥶, 𣐾, 烌, 𪻜, 䏫, 𫃢, 𮔄, 䛙, 貅, 𮔏, 銝, 𩗆, 䮌, 鮴, 𪘆
- 𠉟, 𠏕, 𩢮, 鵂(鸺), 𭓭, 茠, 𩂯, 髹, 庥, 㾋, 恷, 𤈢, 烋, 𪀪, 𰂥
References
[edit]- Kangxi Dictionary: page 96, character 2
- Dai Kanwa Jiten: character 440
- Dae Jaweon: page 203, character 2
- Hanyu Da Zidian (first edition): volume 1, page 117, character 18
- Unihan data for U+4F11
Chinese
[edit]| simp. and trad. |
休 | |
|---|---|---|
Glyph origin
[edit]| Historical forms of the character 休 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Shang | Western Zhou | Shuowen Jiezi (compiled in Han) | Liushutong (compiled in Ming) |
| Oracle bone script | Bronze inscriptions | Small seal script | Transcribed ancient scripts |
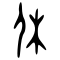
|

|

|

|
|
References:
Mostly from Richard Sears' Chinese Etymology site (authorisation),
| |||
Ideogrammic compound (會意 / 会意): 人 (“man”) + 木 (“tree”) – a man leaning against a tree, resting.
Etymology 1
[edit](This etymology is missing or incomplete. Please add to it, or discuss it at the Etymology scriptorium.)
Pronunciation
[edit]- Mandarin
- Cantonese
- Gan (Wiktionary): xiu1
- Hakka
- Jin (Wiktionary): xiou1
- Northern Min (KCR): hiú
- Eastern Min (BUC): hiĕu
- Puxian Min (Pouseng Ping'ing): hiu1
- Southern Min
- Wu (Northern, Wugniu): 1shieu
- Xiang (Changsha, Wiktionary): xiou1
- Mandarin
- (Standard Chinese)+
- Hanyu Pinyin: xiū
- Zhuyin: ㄒㄧㄡ
- Tongyong Pinyin: siou
- Wade–Giles: hsiu1
- Yale: syōu
- Gwoyeu Romatzyh: shiou
- Palladius: сю (sju)
- Sinological IPA (key): /ɕi̯oʊ̯⁵⁵/
- (Dungan)
- Cyrillic and Wiktionary: щю (xi͡u, I)
- Sinological IPA (key): /ɕiou²⁴/
- (Note: Dungan pronunciation is currently experimental and may be inaccurate.)
- (Standard Chinese)+
- Cantonese
- (Standard Cantonese, Guangzhou–Hong Kong)
- Jyutping: jau1
- Yale: yāu
- Cantonese Pinyin: jau1
- Guangdong Romanization: yeo1
- Sinological IPA (key): /jɐu̯⁵⁵/
- (Taishanese, Taicheng)
- Wiktionary: hiu1
- Sinological IPA (key): /hiu³³/
- (Standard Cantonese, Guangzhou–Hong Kong)
- Gan
- (Nanchang)
- Wiktionary: xiu1
- Sinological IPA (key): /ɕiu⁴²/
- (Nanchang)
- Hakka
- (Sixian, incl. Miaoli and Neipu)
- Pha̍k-fa-sṳ: hiû
- Hakka Romanization System: hiuˊ
- Hagfa Pinyim: hiu1
- Sinological IPA: /hi̯u²⁴/
- (Meixian)
- (Sixian, incl. Miaoli and Neipu)
- Jin
- (Taiyuan)+
- Wiktionary: xiou1
- Sinological IPA (old-style): /ɕiəu¹¹/
- (Taiyuan)+
- Northern Min
- (Jian'ou)
- Kienning Colloquial Romanized: hiú
- Sinological IPA (key): /xiu⁵⁴/
- (Jian'ou)
- Eastern Min
- (Fuzhou)
- Bàng-uâ-cê: hiĕu
- Sinological IPA (key): /hieu⁵⁵/
- (Fuzhou)
- Puxian Min
- (Putian)
- Pouseng Ping'ing: hiu1
- Báⁿ-uā-ci̍: hiu
- Sinological IPA (key): /hiu⁵³³/
- (Xianyou)
- Pouseng Ping'ing: hiu1
- Sinological IPA (key): /hiu⁵⁴⁴/
- (Putian)
- Southern Min
- Wu
- Xiang
- (Changsha)
- Wiktionary: xiou1
- Sinological IPA (key): /ɕi̯əu̯³³/
- (Changsha)
- Dialectal data
- Middle Chinese: xjuw
- Old Chinese
- (Baxter–Sagart): /*qʰ(r)u/
- (Zhengzhang): /*qʰu/
Definitions
[edit]休
- to rest; to relax
- joyous; happy
- (archaic, literary) glory; virtue; goodness (what is worthy of praise and celebration)
- 虎拜稽首,對揚王休。 [Pre-Classical Chinese, trad.]
- From: The Classic of Poetry, c. 11th – 7th centuries BCE, translated based on James Legge's version
- Hǔ bài qǐshǒu, duì yáng Wáng xiū. [Pinyin]
- Hu bowed with his head to the ground,
And in response displayed the goodness of the King.
虎拜稽首,对扬王休。 [Pre-Classical Chinese, simp.]
- (archaic, literary) bliss; auspicious omen
- 此三子者,皆布衣之士也;懷怒未發,休祲降於天,與臣而將四矣。 [Classical Chinese, trad.]
- From: Zhanguo Ce, circa 5th – 3rd centuries BCE
- Cǐ sān zǐ zhě, jiē bùyī zhī shì yě; huái nù wèi fā, xiū jìn jiàng yú tiān, yǔ chén ér jiāng sì yǐ. [Pinyin]
- All of those three worthy men were heroes among humble commoners who, having not even released their wrath, saw omens auspicious to their heroic deeds and ruinous to their opponents dispatched by Heaven. Now, with me, there is about to be a fourth.
此三子者,皆布衣之士也;怀怒未发,休祲降于天,与臣而将四矣。 [Classical Chinese, simp.]
- to stop; to cease
- 喋喋不休 ― diédiébùxiū ― to talk endlessly
- to retire
- (historical) to cast off one’s wife and send her home; to divorce one's wife
- do not; don't
- 心事莫將和淚説,鳳笙休向淚時吹。腸斷更無疑! [Ci, trad.]
- From: c. 975~978, 李煜 (Li Yu),《望江南》, translated by Xu Yuanchong
- Xīnshì mò jiāng hé lèi shuō, fèngshēng xiū xiàng lèi shí chuī. Chángduàn gèng wúyí! [Pinyin]
- Don't ask about my grief of recent years nor play on flute when tears come out, or else my heart would break, no doubt!
心事莫将和泪说,凤笙休向泪时吹。肠断更无疑! [Ci, simp.]
- a surname
- A transliteration of the English male given name Hugh
- 休·傑克曼/休·杰克曼 ― Xiū Jiékèmàn ― Hugh Jackman
Compounds
[edit]- 不休 (bùxiū)
- 不眠不休 (bùmiánbùxiū)
- 不肯干休
- 不能自休
- 中休 (zhōngxiū)
- 乞休
- 介休 (Jièxiū)
- 休休
- 休假 (xiūjià)
- 休克 (xiūkè)
- 休兵 (xiūbīng)
- 休刊 (xiūkān)
- 休命
- 休咎
- 休士頓市 / 休士顿市
- 休妻 (xiūqī)
- 休嫌
- 休學 / 休学 (xiūxué)
- 休屠 (Xiūtú)
- 休崙湖 / 休仑湖
- 休市 (xiūshì)
- 休徵 / 休征
- 休怪
- 休息
- 休息室
- 休想 (xiūxiǎng)
- 休憩 (xiūqì)
- 休戈
- 休戚 (xiūqī)
- 休戚相關 / 休戚相关 (xiūqīxiāngguān)
- 休戚與共 / 休戚与共 (xiūqīyǔgòng)
- 休戰 / 休战 (xiūzhàn)
- 休提
- 休明
- 休暇 (xiūxiá)
- 休書 / 休书 (xiūshū)
- 休會 / 休会 (xiūhuì)
- 休業 / 休业 (xiūyè)
- 休業式 / 休业式
- 休歇 (xiūxiē)
- 休止 (xiūzhǐ)
- 休止符 (xiūzhǐfú)
- 休沐
- 休漁期 / 休渔期 (xiūyúqī)
- 休火山 (xiūhuǒshān)
- 休烈
- 休牛放馬 / 休牛放马
- 休牛散馬 / 休牛散马
- 休牛歸馬 / 休牛归马
- 休眠 (xiūmián)
- 休眠期
- 休眠火山 (xiūmián huǒshān)
- 休管
- 休耕 (xiūgēng)
- 休職 / 休职 (xiūzhí)
- 休致 (xiūzhì)
- 休診 / 休诊 (xiūzhěn)
- 休閒 / 休闲 (xiūxián)
- 休閒活動 / 休闲活动
- 休離 / 休离
- 休養 / 休养 (xiūyǎng)
- 休養生息 / 休养生息 (xiūyǎngshēngxī)
- 何休
- 便休
- 公休 (gōngxiū)
- 刺刺不休
- 勒休
- 同休共戚
- 呶呶不休 (náonáobùxiū)
- 喋喋不休 (diédiébùxiū)
- 善罷干休
- 善罷甘休 / 善罢甘休 (shànbàgānxiū)
- 天休 (tiānxiū)
- 奪休 / 夺休
- 官休
- 干休 (gānxiū)
- 意休不休
- 按甲休兵
- 旬休
- 更休
- 棘棘不休
- 榮休 / 荣休 (róngxiū)
- 欲說還休 / 欲说还休
- 欲語還休 / 欲语还休
- 歸休 / 归休
- 無了無休 / 无了无休
- 無疆之休 / 无疆之休
- 無盡無休 / 无尽无休 (wújìnwúxiū)
- 燠休
- 甘休 (gānxiū)
- 病休 (bìngxiū)
- 皮日休
- 萬事皆休 / 万事皆休
- 紹休聖緒 / 绍休圣绪
- 絮絮不休
- 罷休 / 罢休 (bàxiū)
- 耶律休哥
- 至死方休
- 與國同休 / 与国同休
- 與民休息 / 与民休息
- 西合休 (Xīhéxiū)
- 解甲休兵
- 解甲休士
- 討休 / 讨休
- 話休絮煩 / 话休絮烦
- 誓不甘休
- 貫休 / 贯休
- 買休 / 买休
- 買休賣休 / 买休卖休
- 輪休 / 轮休 (lúnxiū)
- 退休 (tuìxiū)
- 退休金 (tuìxiūjīn)
- 長休告 / 长休告
- 長休飯 / 长休饭
- 雖休勿休 / 虽休勿休
- 離休 / 离休 (líxiū)
- 風休冰解 / 风休冰解
Etymology 2
[edit]Pronunciation
[edit]- Mandarin
- (Standard Chinese)+
- Hanyu Pinyin: xǔ
- Zhuyin: ㄒㄩˇ
- Tongyong Pinyin: syǔ
- Wade–Giles: hsü3
- Yale: syǔ
- Gwoyeu Romatzyh: sheu
- Palladius: сюй (sjuj)
- Sinological IPA (key): /ɕy²¹⁴/
- (Standard Chinese)+
Definitions
[edit]休
Compounds
[edit]References
[edit]- “休”, in 教育部臺灣台語常用詞辭典 [Dictionary of Frequently-Used Taiwanese Taigi] (overall work in Mandarin and Hokkien), Ministry of Education, R.O.C., 2025.
- Proper Names And Translation Service, Xinhua News Agency, editor (1993), “Hugh 休”, in 世界人名翻译大辞典 [Names of The Worlds Peoples: A comprehensive dictionary of names in Roman-Chinese] (in Chinese), Beijing: China Translation & Publishing Corporation, →ISBN, →OCLC, page 1315: “西方男子教名,亦作姓用”.
- 莆田市荔城区档案馆 [Putian City Licheng District Archives], editor (2022), “休”, in 莆仙方言文读字汇 [Puxian Dialect Literary Reading Dictionary] (overall work in Mandarin and Puxian Min), page 266.
Japanese
[edit]See also 休する
Kanji
[edit]休
Readings
[edit]- Go-on: く (ku)
- Kan-on: きゅう (kyū, Jōyō)←きう (kiu, historical)
- Kun: やすまる (yasumaru, 休まる, Jōyō)、やすむ (yasumu, 休む, Jōyō)、やすめる (yasumeru, 休める, Jōyō)、いこう (ikou, 休う)←いこふ (ikofu, 休ふ, historical)、やすみ (yasumi, 休み)、やすらい (yasurai, 休らい)←やすらひ (yasurafi, 休らひ, historical)、やすらう (yasurau, 休らう)←やすらふ (yasurafu, 休らふ, historical)、やむ (yamu, 休む)、やめる (yameru, 休める)、ゆくゆく (yukuyuku, 休く)、よい (yoi, 休い)
- Nanori: たね (tane)、のぶ (nobu)、やす (yasu)、やすみ (yasumi)、やすむ (yasumu)、よし (yoshi)
Noun
[edit]Compounds
[edit]Compounds containing 休
- 休意 (kyūi, “peace, tranquility”)
- 休演 (kyūen, “suspending performance”)
- 休暇 (kyūka, “holiday, day off”)
- 休火山 (kyūkazan, “dormant volcano”)
- 休会 (kyūkai, “adjournment, recess”)
- 休学 (kyūgaku, “suspension of studies”)
- 休刊 (kyūkan, “suspension of publication”)
- 休閑 (kyūkan, “fallowing”)
- 休館 (kyūkan, “library or museum closure”)
- 休漁 (kyūryō, “suspension of fishing”)
- 休業 (kyūgyō, “business closure”)
- 休憩 (kyūkei, “rest”)
- 休校 (kyūkō, “school closure”)
- 休耕 (kyūkō, “lying fallow”)
- 休航 (kyūkō, “suspension of sailing”)
- 休講 (kyūkō, “canceled lecture”)
- 休載 (kyūsai, “suspension of publication”)
- 休止 (kyūshi, “pause”)
- 休祥 (kyūshō, “good omen”)
- 休場 (kyūjō, “theater closure, stage absence”)
- 休職 (kyūshoku, “suspension from office”)
- 休心 (kyūshin, “rest assured”)
- 休診 (kyūshin, “temporary closing of doctor's office”)
- 休錘 (kyūsui, “suspension of fabric factory operations”)
- 休戚 (kyūseki, “joy and sorrow”)
- 休戦 (kyūsen, “truce, armistice”)
- 休息 (kyūsoku, “rest, relaxation”)
- 足休 (ashiyasume, “resting feet”)
- 休怠 (kyūtai, “laziness”)
- 休廷 (kyūtei, “court recess”)
- 休転 (kyūten, “suspension of operations”)
- 休電 (kyūden, “electricity outage”)
- 休日 (kyūjitsu, “holiday, day off”)
- 休泊所 (kyūhakujo, “resting place”)
- 休符 (kyūfu, “rest (in music)”)
- 休眠 (kyūmin, “idle”)
- 休養 (kyūyō, “rest”)
- 運休 (unkyū)
Related terms
[edit]Korean
[edit]Etymology
[edit]From Middle Chinese 休 (MC xjuw).
Historical readings
- Recorded as Middle Korean 휴ᇢ (Yale: hyuw) in Dongguk Jeongun (東國正韻 / 동국정운), 1448.
- Recorded as Middle Korean 휴 (hywu) (Yale: hyu) in Sinjeung Yuhap (新增類合 / 신증유합), 1576.
Pronunciation
[edit]- (SK Standard/Seoul) IPA(key): [çu]
- Phonetic hangul: [휴]
Hanja
[edit]Compounds
[edit]References
[edit]- 국제퇴계학회 대구경북지부 (國際退溪學會 大邱慶北支部) (2007). Digital Hanja Dictionary, 전자사전/電子字典. [1]
Vietnamese
[edit]Han character
[edit]- This term needs a translation to English. Please help out and add a translation, then remove the text
{{rfdef}}.
References
[edit]Categories:
- CJK Unified Ideographs block
- Han script characters
- Enclosed CJK Letters and Months block
- Translingual lemmas
- Translingual symbols
- Han ideogrammic compounds
- Chinese lemmas
- Mandarin lemmas
- Dungan lemmas
- Cantonese lemmas
- Taishanese lemmas
- Gan lemmas
- Hakka lemmas
- Jin lemmas
- Northern Min lemmas
- Eastern Min lemmas
- Hokkien lemmas
- Teochew lemmas
- Puxian Min lemmas
- Wu lemmas
- Xiang lemmas
- Middle Chinese lemmas
- Old Chinese lemmas
- Chinese hanzi
- Mandarin hanzi
- Dungan hanzi
- Cantonese hanzi
- Taishanese hanzi
- Gan hanzi
- Hakka hanzi
- Jin hanzi
- Northern Min hanzi
- Eastern Min hanzi
- Hokkien hanzi
- Teochew hanzi
- Puxian Min hanzi
- Wu hanzi
- Xiang hanzi
- Middle Chinese hanzi
- Old Chinese hanzi
- Chinese verbs
- Mandarin verbs
- Dungan verbs
- Cantonese verbs
- Taishanese verbs
- Gan verbs
- Hakka verbs
- Jin verbs
- Northern Min verbs
- Eastern Min verbs
- Hokkien verbs
- Teochew verbs
- Puxian Min verbs
- Wu verbs
- Xiang verbs
- Middle Chinese verbs
- Old Chinese verbs
- Chinese adjectives
- Mandarin adjectives
- Dungan adjectives
- Cantonese adjectives
- Taishanese adjectives
- Gan adjectives
- Hakka adjectives
- Jin adjectives
- Northern Min adjectives
- Eastern Min adjectives
- Hokkien adjectives
- Teochew adjectives
- Puxian Min adjectives
- Wu adjectives
- Xiang adjectives
- Middle Chinese adjectives
- Old Chinese adjectives
- Chinese interjections
- Mandarin interjections
- Dungan interjections
- Cantonese interjections
- Taishanese interjections
- Gan interjections
- Hakka interjections
- Jin interjections
- Northern Min interjections
- Eastern Min interjections
- Hokkien interjections
- Teochew interjections
- Puxian Min interjections
- Wu interjections
- Xiang interjections
- Middle Chinese interjections
- Old Chinese interjections
- Chinese proper nouns
- Mandarin proper nouns
- Dungan proper nouns
- Cantonese proper nouns
- Taishanese proper nouns
- Gan proper nouns
- Hakka proper nouns
- Jin proper nouns
- Northern Min proper nouns
- Eastern Min proper nouns
- Hokkien proper nouns
- Teochew proper nouns
- Puxian Min proper nouns
- Wu proper nouns
- Xiang proper nouns
- Middle Chinese proper nouns
- Old Chinese proper nouns
- Chinese nouns
- Mandarin nouns
- Dungan nouns
- Cantonese nouns
- Taishanese nouns
- Gan nouns
- Hakka nouns
- Jin nouns
- Northern Min nouns
- Eastern Min nouns
- Hokkien nouns
- Teochew nouns
- Puxian Min nouns
- Wu nouns
- Xiang nouns
- Middle Chinese nouns
- Old Chinese nouns
- Chinese terms with IPA pronunciation
- Chinese terms spelled with 休
- Mandarin terms with usage examples
- Chinese terms with archaic senses
- Chinese literary terms
- Literary Chinese terms with quotations
- Chinese terms with historical senses
- Chinese surnames
- Chinese renderings of English male given names
- Chinese terms derived from English
- Chinese terms borrowed from English
- Chinese obsolete forms
- Japanese kanji
- Japanese first grade kanji
- Japanese kyōiku kanji
- Japanese jōyō kanji
- Japanese kanji with goon reading く
- Japanese kanji with kan'on reading きゅう
- Japanese kanji with historical kan'on reading きう
- Japanese kanji with kun reading やす・まる
- Japanese kanji with kun reading やす・む
- Japanese kanji with kun reading やす・める
- Japanese kanji with kun reading いこ・う
- Japanese kanji with historical kun reading いこ・ふ
- Japanese kanji with kun reading やす・み
- Japanese kanji with kun reading やす・らい
- Japanese kanji with historical kun reading やす・らひ
- Japanese kanji with kun reading やす・らう
- Japanese kanji with historical kun reading やす・らふ
- Japanese kanji with kun reading や・む
- Japanese kanji with kun reading や・める
- Japanese kanji with kun reading ゆくゆ・く
- Japanese kanji with kun reading よ・い
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading たね
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading のぶ
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading やす
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading やすみ
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading やすむ
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading よし
- Japanese lemmas
- Japanese nouns
- Japanese terms spelled with first grade kanji
- Japanese terms with 1 kanji
- Japanese terms spelled with 休
- Japanese single-kanji terms
- Korean terms derived from Middle Chinese
- Middle Korean hanja
- Korean lemmas
- Korean hanja
- Korean hanja forms
- Vietnamese lemmas
- Vietnamese Han characters























































































